Hoarseness
Hoarseness is alteration of voice due to disorder over the vocal cords or voice box. The commonest cause of hoarseness is acute laryngitis which is usually occur during upper respiratory tract infection. This condition is usually self limiting and the voice usually normalised in less than a week but could be prolonged up to two weeks in patient who strained his voice during the episodes.
Other common benign vocal cord lesions would be vocal cord nodules which is also called “singers nodules” due to the over use and abuse of voice. Polyp and cyst of vocal cord also might occur in the misuse of voice but it sometimes could be seen in those who do not.
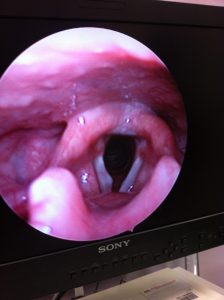
Right Vocal Cord Cyst
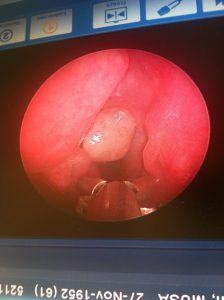
Posterior Commisure Granuloma which is usually due to intubational injury. However, tuberculous infection have to be rule out.
In vocal cord haemorrhage, patient might experience sudden hoarseness after strenuous voice usage. It is due to the ruptured of blood vessel overlying the surface of the vocal cords.
In laryngopharyngeal reflux, the gastric acid could reflux up to the pharynx and larynx and cause edema or swelling of the vocal cords. Chronic heavy smoker and patient which have prolonged exposure to hot fumes might also suffered from edema of the vocal cords.
Other causes of hoarseness includes neurological disorders such as Parkinson and stroke. Vocal cord paralysis and spasmodic dysphonia might also cause voice disorder. In vocal cord palsy, a third of the it is cause by viral infection and another one third is due to malignancy. The remaining one third is usually due to unknown reason.
In Malaysia, laryngeal tuberculosis could be one of the cause of hoarseness and might be the only presentation of tuberculosis infection.
The sinister diagnosis of laryngeal cancer or tumour should be ruled out especially in chronic smokers and chronic alcoholics.
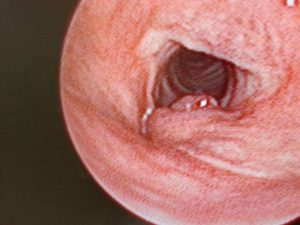
Left vocal cord tumour
When should hoarseness be of concern ?
-Hoarseness that prolonged more than 2-3 weeks.
-Hoarseness that associated with choking sensation when eating
-Hoarseness which is accompanied by loss of weight, loss of appetite, night sweat and chronic cough
-Hoarseness that is associated with neck swelling or mass
– Pain when swallowing
A complete history and physical examination with endoscopic or fiber-optic examination of larynx is crucial to ascertain the diagnosis.
Treatment depends on the diagnosis:
Vocal cord nodules could resolved with voice therapy and voice rest
Laryngo-pharyngeal reflux is treated with anti-reflux therapy
Vocal cord Cyst should be excised via micro-laryngeal surgery
If suspicious of laryngeal carcinoma or tuberculosis a biopsy should be done under General anaesthesia to achieved the correct diagnosis.